Creating an Object
In this chapter, you will learn how to create an object and the initialization process.
Initialization
Initialization is the process of preparing an instance of a class. This process involves setting an initial value for each instance variable on that instance. Any required setup is also performed before the new instance is ready for use. For the car example, it will answer questions such as:
- How many doors?
- What is the color?
- Auto or Manual transmission?
We can say:
door = 2
color = 'red'
transmission = 'auto'

The code answers those questions by initializing the variables. How do we initialize instance variables? Where do we initialize them? Let's discuss about them now.
Instance Variable
An instance variable has a name beginning with @. The instance variables comprise the state unique to an object. We can have two car objects with different colors such as red and black. Let's say that the instances of the Car class have an instance variable called color. We can initialize the color instance variable like this:
class Car
def initialize(color)
@color = color
end
end
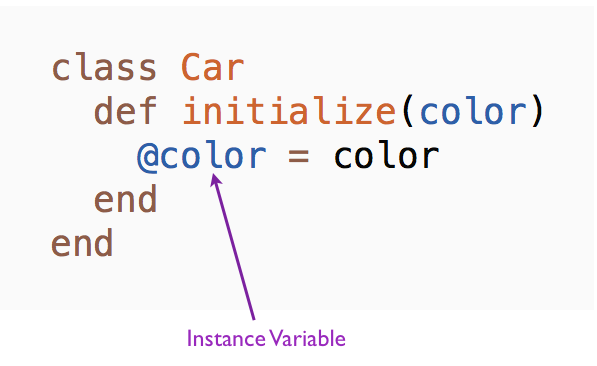
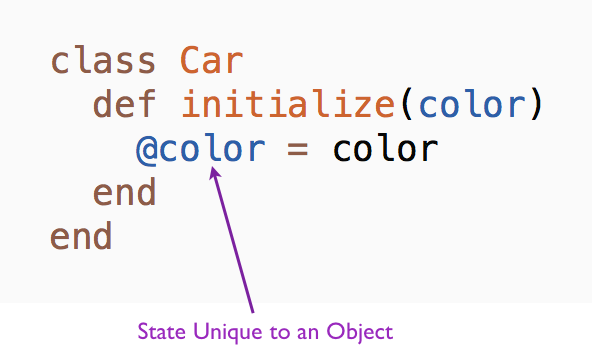
The parameters to the initialize method is used to assign initial values to the attributes of an object. Instance variables spring into existence when they are initialized for the first time. In this example, we initialize the color instance variable @color in the initialize method. We can now create an instance of a car object with a specific color.
car = Car.new('red')
We send the new() message to the Car class with the color red as the argument.
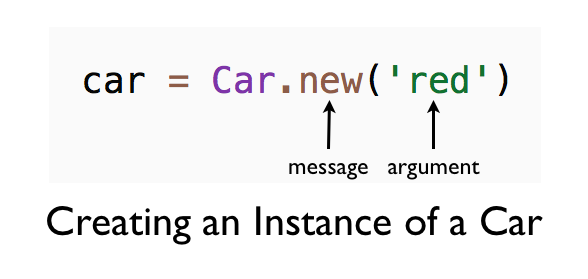
Ruby calls the initialize method with red as the argument. In the initialize method, we store the value of color, red, in the instance variable @color.
Fabio Asks
What happens if you call the initialize method?
Let's call the initialize method.
Car.initialize('black')
You will get the error:
NoMethodError: private method ‘initialize’ called for Car:Class
We cannot call the initialize method. Only Ruby can call it. To initialize an instance of any class, always use the new method.
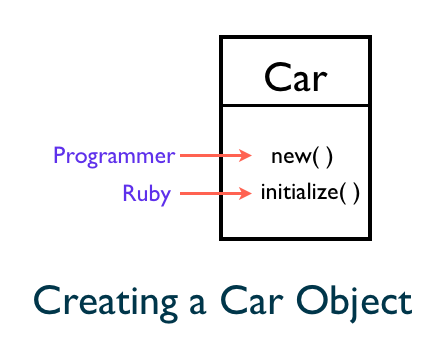
Uninitialized Instance Variables
Instance variables have nil value if they are not initialized. The nil represents the concept of nothing in Ruby. Let's look at an example.
class Car
def initialize(color)
@color = color
end
def price
@price
end
def drive
return 'driving'
end
end
c = Car.new('red')
p c.price
This prints nil. The Car class has a new method called price that returns the price instance variable of the car. Since it was not initialized anywhere in the Car class, it has nil value.
Rhonda Asks
Why is it called an instance variable?
Because the variable is unique to a specific instance of a class.
Summary
In this chapter, you learned about the initialization of an object. Initialization process instantiates a specific object with certain attributes.