Code Execution
In this chapter we will answer the question, when does Ruby execute code as it encounters the code?
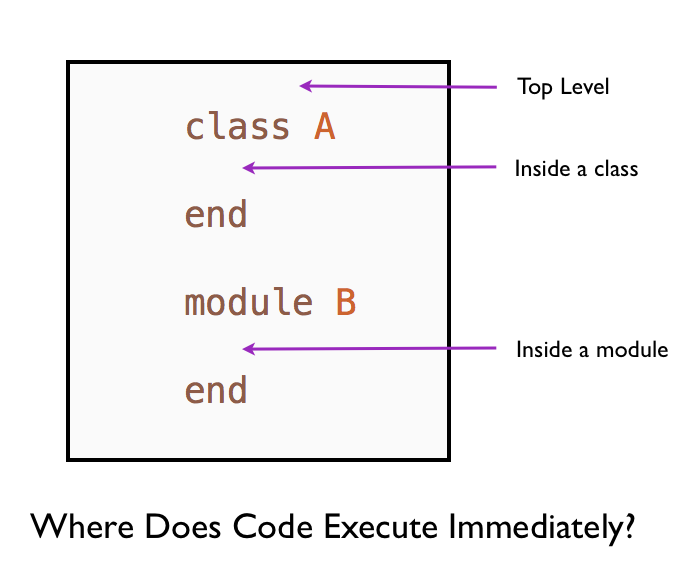
At the Top Level
Open the editor and print 'hi' to the standard output.
puts 'hi'
This prints:
hi
Ruby encountered the puts() method and it executed the instruction. You see the output in the terminal.
Inside a Class
Define a class and print something to the standard output within the class.
class Rabbit
puts "I am within Rabbit class"
end
Running this program prints:
I am within Rabbit class
This dynamic nature of Ruby surprises developers who are familiar with other languages.

Inside a Module
Define a module and print something to the standard output within the module.
module Rabbit
puts "I am within Rabbit module"
end
Running this program prints:
I am within Rabbit module
Inside a Method in a Class
Let's now add a method to the Rabbit class:
class Rabbit
def speak
puts "My name is Bugs Bunny"
end
end
Running this program does not print anything to the standard output.
Invoking the Instance Method
Why? Because, we need an instance of Rabbit to send the speak() message to it.
class Rabbit
def speak
puts "My name is Bugs Bunny"
end
end
bugs = Rabbit.new
bugs.speak
Running this program prints:
My name is Bugs Bunny

Inside a Method in a Module
What happens when we define a method in a module?
module Rabbit
def speak
puts "My name is Bugs Bunny"
end
end
Running this program prints nothing to the standard output.
Mixin the Module
We can mixin the Rabbit module to the top level and invoke the speak() method.
module Rabbit
def speak
puts "My name is Bugs Bunny"
end
end
include Rabbit
speak
Running this program prints:
My name is Bugs Bunny
Summary
In this chapter, we learned that Ruby executes code as it encounters code:
- At the top level.
- Inside a class.
- Inside a module.
But, it does not execute the code inside the instance method defined in a class or a method defined inside a module as it encounters it. We need an object to execute an instance method defined in a class or mixin the method defined in a module and then call the method.