The Method Lookup
In this chapter, you will learn the introspection abilities of Ruby in the context of Ruby Object Model. We will query for ancestors. Class hierarchy determines the method look-up in Ruby.
Define Method in Object
We already know that class Object is the super class of any user defined class. Let's define a greet method by opening the Ruby's built-in Object class.
class Object
def greet
puts 'hi'
end
end
User Defined Class
Let's create a class and call the method greet() on it.
class Greeter
end
g = Greeter.new
g.greet
This prints:
hi
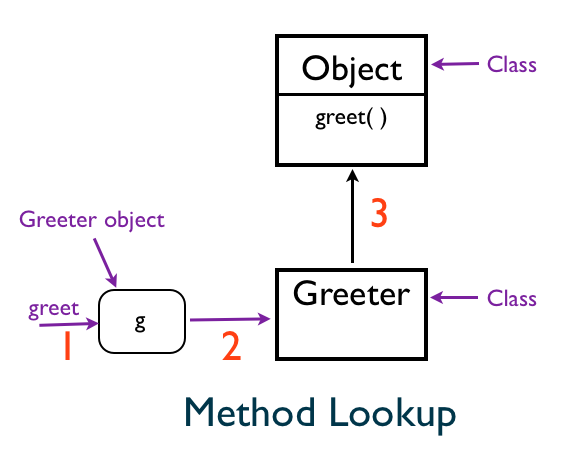
The variable g has an instance of Greeter class. When we call the greet() method, the value of self changes to the Greeter object g. Then Ruby looks for the greet() method in the Greeter class. It does not find it there. It goes to the super-class of Greeter which is the Ruby's built-in Object class. It finds the greet() method in Object class, it calls that method.
Method Lookup Path
We can ask ruby for its method look up path like this:
class Object
def greet
p 'hi'
end
end
class Greeter
end
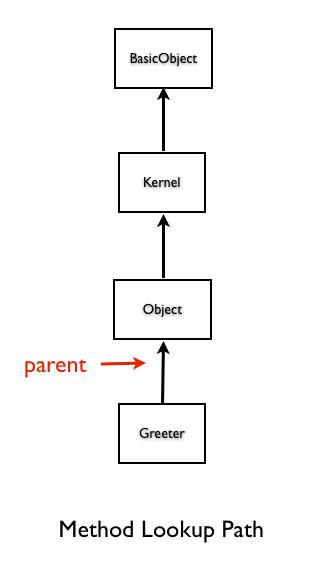
p Greeter.ancestors
This prints:
[Greeter, Object, Kernel, BasicObject].
The order in which the classes and modules appear in the array represents the order in which Ruby searches for the methods. The method look up sequence is as shown below:
- Greeter Class
- Object Class
- Kernel Module
- BasicObject Class

Summary
In this chapter, you learned the introspection abilities of Ruby in the context of Ruby Object Model. We were able to query for ancestors. Why do we need to worry about class hierarchy in Ruby? Because it determines the method look-up in Ruby.