Instance Methods and Instance Variables
In this chapter, you will learn where the instance methods and instance variables live in Ruby.
Greeting Example
Let's look at a simple example that we can use to experiment and learn.
class Greeter
def initialize(text)
@text = text
end
def greet
@text
end
end
greeter = Greeter.new('Hi')
p greeter.class
This prints:
Greeter
Instance Methods of Greeter Class
We know the instance of Greeting; the greeter object gets created using the Greeter class. We can also get the instance methods as follows:
p greeter.class.instance_methods(false)
This prints:
[:greet]
The methods defined in a class becomes instance methods available to the objects of that class.
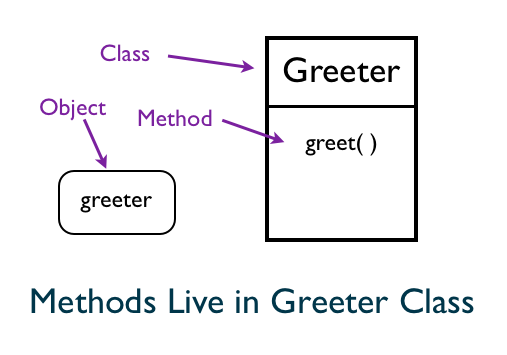
Instance Variables of Greeter Object
Let's look at the instance variables of the object o.
p greeter.instance_variables
This prints:
[:@text]
The instance variables live in the specific objects we create.
Fabio Asks
Can we have many instance variables in a class?
Yes. For instance, we could have text and language as the instance variables.
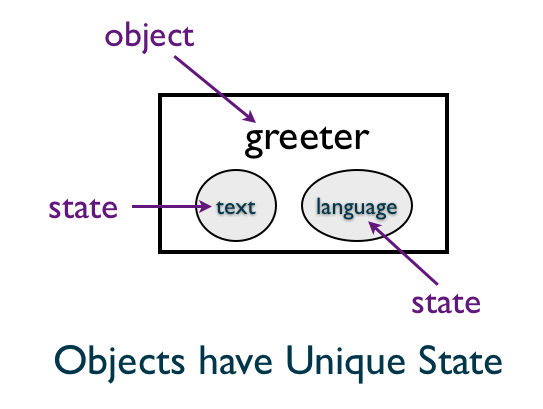
In code, it would look like this:
class Greeter
def initialize(text, language)
@text = text
@language = language
end
def greet
"In #{@language}, it's #{@text}"
end
end
greeter = Greeter.new('Hi', 'English')
p greeter.welcome
This prints:
In English, it's Hi
Instance Methods of String
Ruby's built-in classes also have instance methods. Let's experiment with the Ruby built-in String class.
> s = 'hi'
=> "hi"
> s.instance_methods
NoMethodError: undefined method `instance_methods' for "hi":String
from (irb):3
from /Users/bparanj/.rvm/rubies/ruby-2.3.0/bin/irb:11:in `
We get an error when we call instance_methods on the string object. Let's call instance_methods on the String class.
> String.instance_methods
=> [:<=>, :==, :===, :eql?, :hash, :casecmp, :+, :*, :%, :[], :[]=, :insert, :length, :size, :bytesize, :empty?, :=~, :match, :succ, :succ!, :next, :next!, :upto, ...]
We see lots of methods defined in the String class. Let's call the length method on the string object.
> s.length
=> 2
It prints 2.
Summary
In this chapter, we were able to query for instance variables and instance methods. We learned that the instance methods live in the class and the instance variables live in the object. Objects share instance methods. Instance variables are not shared between objects.